|
5 Primal Tips For Optimizing Meat Consumption Let's just start off with one of the most important item: ENJOY YOUR MEATS! Savor the juices dripping down your chin from a grilled burger. Relish the tenderness of slow roasted chicken. Sink your teeth into the creamy, flaky textures of a perfectly sautéed salmon fillet. In other words, embrace the gastronome experience for everything it can be. Then check these FIVE tips next time you consume protein: 1. Go For Variety Get the full range of nutrients available and minimize the possible risks of eating too much of any one thing. Eat a wide variety of sources, a move that ensures you're getting all the amino acids you need to perform basic physiological processes. A mussel might give you similar amino acids as a chicken thigh, but the similarities end there. The mussel provides manganese, selenium, a ton of B12, and some folate. The chicken thigh provides less B12, some niacin, a little more magnesium. Eat ruminants (beef, bison, lamb, pork). Eat birds such as turkey, chicken, duck. Get some fin fish like salmon, cod, halibut, sardines. Eat shellfish such as oysters, clams, mussels. Eat cephalopods like squid, cuttlefish, octopus. And, yes, even eat insects. After all, they aren't as bad as you imagine. Eating a variety of meats, poultry and fish also minimizes the risk of excess iron-intake. Eating calcium-rich foods with your meat further reduces iron absorption and, in animal studies, reduces the carcinogenicity of dietary heme. 2. Eat Pastured/Wild When Ever Possible Grass-fed and pasture-raised meat is better for you. And more nutrients from a varied, grazing diet as well as a better fatty acid profile. It's also better for the environment, and better for the animal. Choose it when you can, but know an otherwise nutrient-dense diet and wise supplementation can cover your bases regardless. 3. Slow Cook When You Can Slow cooking (less than 375 ºF) minimizes the production of carcinogens associated with cooked meat. Studies show this is especially important for those with insulin resistance. Still, if you love grilled meat, don't give up your grilled steaks and chicken. But be more strategic about it. Slow cook much of your meat and use marinades with herbs like rosemary and thyme - the top two herbs for reducing heterocyclic amines. 4. Eat Vegetables (and Favor Prebiotic Fiber) Variety matters for more than just meat. Vegetables and fruits are sources of vitamins and phytonutrients that meat just can't offer to the same degree. And then there's gut health. The oft-cited study used to criticize keto, for example, was a diet of cold cuts, bacon and cheese. In other words, a diet bereft of vegetables and gut-nourishing prebiotic fiber. Plus, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli counteract the formation of potentially harmful meaty compounds in the gut. By the way, coffee, tea, and red wine also have similar effects (although we don't often think of them as plants, these drinks are made from plants). Try to buy organic whenever possible! 5. Eat Collagen, Too Meat is one of the richest sources of methionine, an essential amino acid. But there's evidence that excessive methionine can depress lifespan and that putting rats on a low-methionine diet extends their life. Collagen is the single best source of glycine, an amino acid that "balances" methionine. In those same rats, adding glycine to a methionine-rich diet restores longevity. You can accomplish this by eating collagenous cuts, like ears, feet, skin, tails, and shanks. You can do this by using supplementary collagen (or eating foods that contain it).
0 Comments
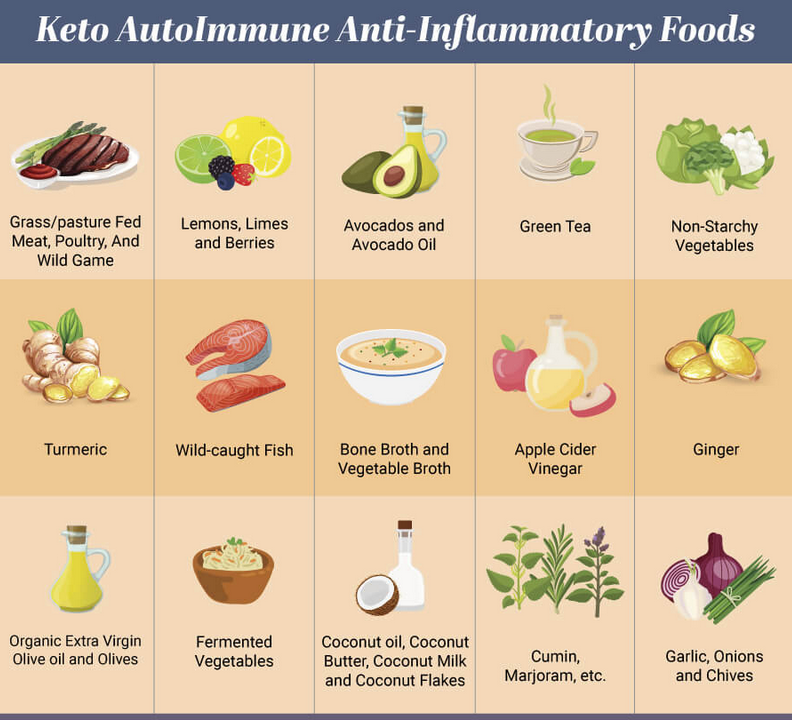
Top 12 Best Foods to Reduce Inflammation To prevent, improve, or heal from an autoimmune condition, it is critical to reduce the inflammation in your body. Choosing the right foods to nourish your body is one of the most critical factors for reducing inflammation and preventing or improving autoimmune conditions. The foods you consume every day have the power to heal your body or to harm and inflame your body. To lower inflammation and improve autoimmunity, you should eliminate pro-inflammatory foods that may be triggering an immune response. Replace those foods with the 12 best foods to reduce inflammation. See list below. What is an Autoimmune Condition? Your immune system is your body’s defense mechanism. It is designed to protect you from disease and other potentially harmful foreign invaders. When functioning properly, the immune system identifies and destroys threats such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites. An autoimmune condition occurs when the body’s immune system turns on its own cells and tissues. The immune system mistakenly identifies the healthy cells and tissues as foreign invaders and mounts an attack to destroy them. This can happen in almost any part of the body, including the brain, muscles, skin, and other organs. Food Sensitivities and Autoimmunity The gut is critically important with autoimmune conditions because gut bacteria heavily regulate your immune system. In fact, 70% of your immune system resides in your gut. One of the main ways that the factors above lead to autoimmunity is by inflaming and damaging the gut and destroying the beneficial bacteria. When the gut lining is damaged, it can become porous. Foods and other things that you are consuming pass through these holes in the gut lining and into your bloodstream. Your immune system is exposed to these foods and reacts to the foods as a threat, amplifying the immune response. Anti-Inflammatory Diet and Autoimmune Conditions A major contributor to autoimmune conditions is inflammation. One of the leading causes of inflammation is a poor diet such as the Standard American Diet (SAD). The foods included in the Standard American Diet (SAD) diet are extremely inflammatory. They contain high levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), or glycotoxins. These compounds cause inflammation and oxidative stress, damaging tissue throughout the body. Top 12 AutoImmune Diet Foods to Reduce Inflammation The autoimmune diet focuses on real whole foods that are the least likely to trigger an immune reaction. Deficiencies in antioxidants, vitamins, and micronutrients can affect the body’s ability to resolve inflammation. Consuming micronutrient rich foods can help to reduce inflammation, support your immune system, and improve autoimmune conditions. It is also important to make sure these foods are organic because pesticides have been linked to autoimmune conditions Here the list of the top 12 foods:
Full details and references - click here. |
Author
DannyTheCoach Archives
January 2023
Categories
All
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed